Do you have an idea for a new electronic hardware product and are wondering how to get started with producing it? The best way to get a product started is to create a prototype, sometimes more than one. There are various methods of creating a prototype. The first two technologies in this article work for the electronics part of your product and the other three technologies are methods for producing a prototype for the casing of your product.
Electronic Development Kits
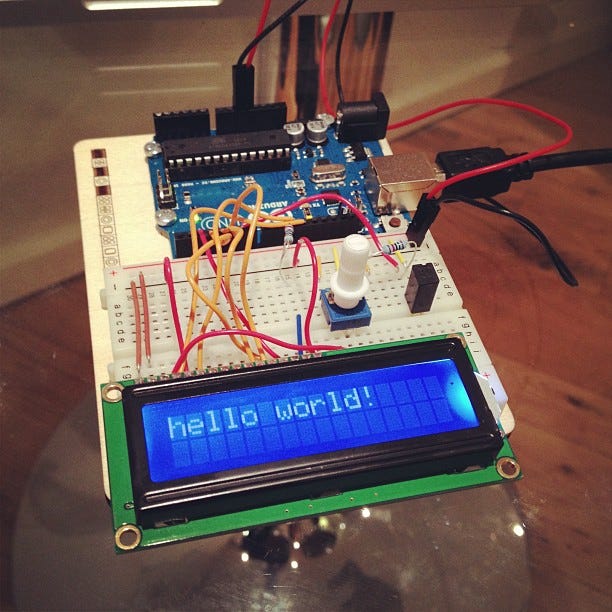
One of the simplest ways to prototype your new electronic hardware product is to use electronic development kits (EDK). Electronic development kits are boards that you can use to create a program or application or to evaluate how your product will perform1. EDKs can range in price from under $50 to $150 or more, depending on the features of the kit’s board2.
Development kits can be used in many areas. Applications include automotive, imaging, communications, and audio. Other applications include wireless, RFID, and motor controls. On the lower price end, function may be limited. At the higher price range, however, features could include USB ports, video or ethernet connections and higher pin counts. Others on the pricier end, like the Adafruit Flora, can be used to add LEDs to clothing, such as shirts, hats, and jackets, or can be controlled by smartphone apps and Bluetooth2. With EDKs you can create your own proof-of-concept prototype to get an idea of how your product will perform and gather interest from potential investors.

Adafruit Flora Board
Printed Circuit Boards (PCB)
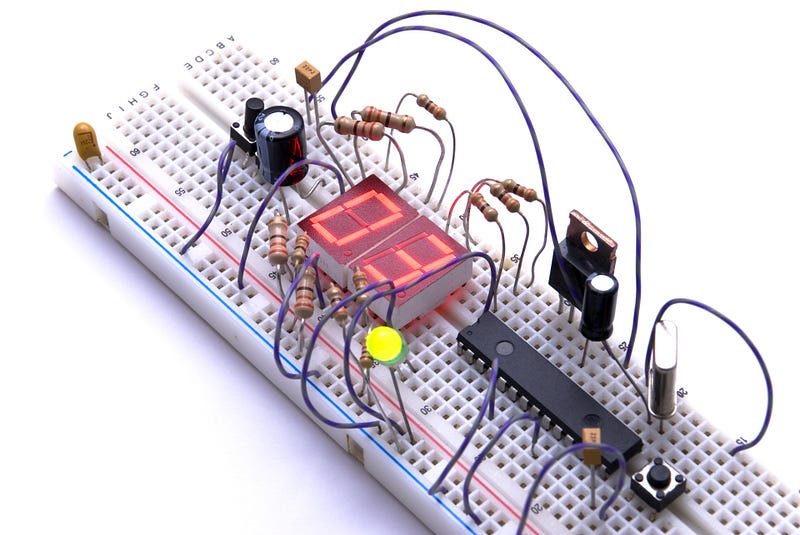
Another way to prototype your new electronic hardware product is to use breadboards, perfboards, and/or printed circuit boards or PCBs. Breadboards can be used to quickly try out your electronic hardware idea and make sure it works. Perfboards are rigid sheets with holes to which you add components, such as resistors or integrated circuits, by soldering3. PCBs take longer and require a bit more effort, but are more permanent and look better. You can use breadboards and perfboards to test your design and determine if any improvements are necessary. Depending on the design and function of your product, the more permanent PCB can be used as your final product in some cases4.
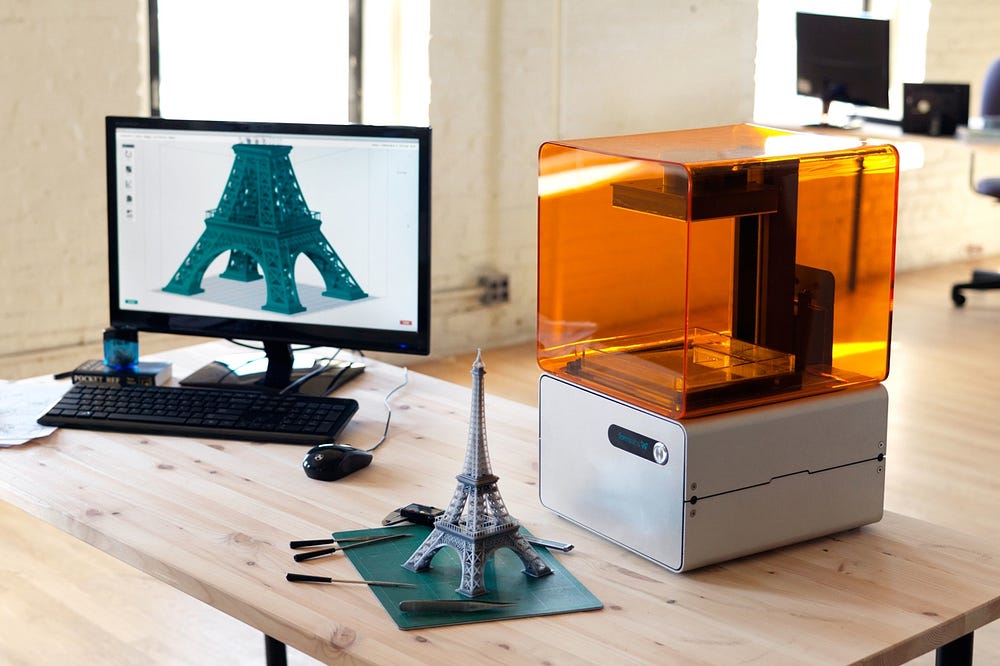
Stereolithography (SLA)
A third method of prototyping your new electronic hardware product is a type of 3D printing known as stereolithography. A stereolithography apparatus (SLA) is a machine that uses light to harden a liquid plastic into detailed, professional looking prototypes or products. The photopolymerization process produces strong, durable prototypes because of the chemical bonds created between the plastic layers5. SLA is a quick and relatively inexpensive method to create accurately shaped pieces, even when the pieces have an odd shape or intricate designs.
SLA machines are more expensive than the desktop type 3D printers and can cost in the thousands of dollars5. If you don’t have the budget to purchase an SLA you can hire one of several online companies to produce the prototype for you.

Stereolithography
CNC Machining
A fourth approach to prototyping your product is CNC machining. 3D printing or SLA production are additive processes while CNC machining is a subtractive process. CNC machines start with a block of metal or plastic and then use tools controlled by a computer to precisely remove material to form the product6. Creating a prototype with this method can be done faster, cheaper and with more precision.
The advantages of CNC machining are a stronger product since the part is cut from a solid piece of material and the part can be created from metal or plastic. CNC prototypes can also be created from the same material used in the injection-molding process, allowing movement into high volume production without the need to produce another prototype6.

CNC Lathe-NASA
Injection Molding
A final method of prototyping your new electronic hardware product is injection molding. Injection molding consists of creating a mold of your product and injecting, at a high pressure, liquid plastic into the mold. The intricate detail of the part is created by the high pressure used to inject the plastic. Injection molding is the best method to produce a high quality, detailed, prototype that will be identical to the finished product7.
Starting with lower cost metal molds, like aluminum will save money on your prototype. Once your production volume rises, move to stronger steels to create your molds.

Injection molding
Learning about the above technologies can allow you to find the best method to create your prototypes. Creating good prototypes helps you to refine your product design, determine the best production methods, and find the right investors if needed. The 5 technologies for prototyping your new electronic hardware product listed here can help you do all those things and ensure you bring a well-crafted product to market.
Sources
- Future Electronics- http://www.futureelectronics.com/en/development-tools/dev-tool-hardware.aspx
- Hackaday- https://hackaday.com/2011/02/01/what-development-board-to-use/
- Quora– https://www.quora.com/Whats-the-difference-between-PCBs-and-breadboards
- Medium- https://medium.com/@rxseger/notes-on-prototyping-circuit-boards-c5906e637123
- LiveScience- https://www.livescience.com/38190-stereolithography.html
- Product Development Solutions- http://www.1pds.com/implementing-rapid-prototyping-using-cnc-machining/
- Revpart- https://revpart.com/services/molding-services/silicone-rubber-molding/